Why LPG Remains a Preferred Fuel Source Despite New Alternatives?
2025-07-17
As the world shifts towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, many wonder why Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) is still widely used—especially in homes, restaurants, and industries. With the growing availability of electric and induction cooking technologies, solar heating, and even biogas, one might assume LPG would fade into the background. But the reality is quite the opposite. This article explores why LPG continues to be a reliable, practical, and dominant fuel choice, even in 2025 and beyond.
1. What is LPG and How Is It Used Today?
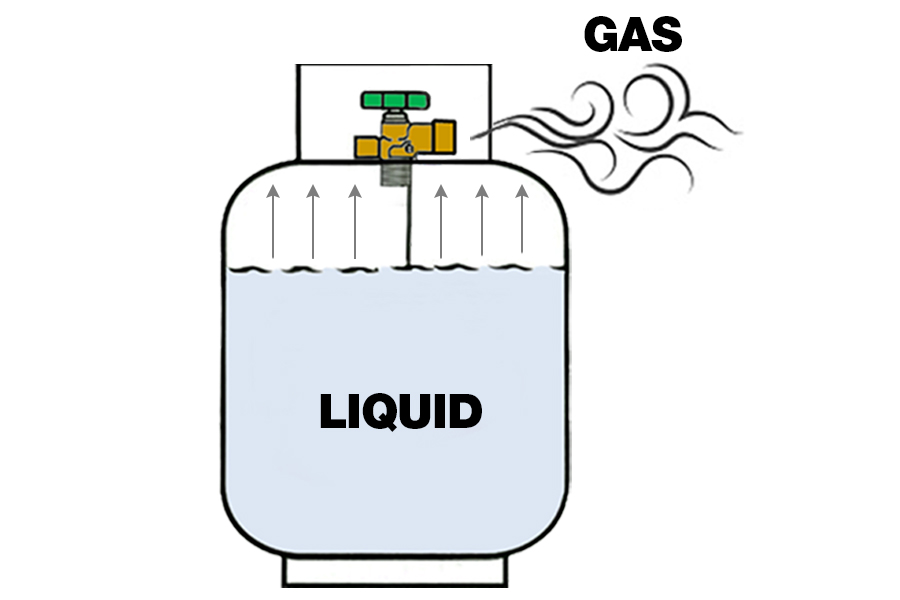
LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) is a flammable mixture of hydrocarbons—primarily propane and butane. It is stored in pressurized cylinders and is commonly used in:
-
Domestic kitchens for cooking
-
Restaurants and food vendors
-
Industrial heating and cutting processes
-
Rural areas without reliable electricity
Its portability and consistent energy output make it a go-to fuel, especially in regions with limited access to modern infrastructure.
2. Benefits of Using LPG as a Fuel
Despite technological advancements, LPG remains preferred for several reasons:
🔹 Clean-burning Fuel
LPG emits fewer pollutants compared to coal, firewood, or kerosene. It produces very little soot and particulate matter, making it safer for indoor use.
🔹 High Calorific Value
LPG offers quick heating due to its high energy output. Boiling or frying is faster compared to electric coils or induction systems.
🔹 Portability
LPG cylinders can be delivered and used without needing a fixed energy grid, making it ideal for rural, remote, or mobile setups.
🔹 Affordability
With government subsidies and competitive pricing, LPG remains cost-effective, especially for middle- and low-income households.
3. Comparison: LPG vs Other Modern Fuels
🔸 3.1 LPG vs Electric Stoves
-
LPG: Instant heat, portable, cheaper per unit.
-
Electric: Safer (no open flame), but slow and dependent on uninterrupted power.
🔸 3.2 LPG vs Induction Cooking
-
LPG: Compatible with all cookware, no need for flat-bottom vessels.
-
Induction: More energy-efficient in ideal conditions but often needs specific pans.
🔸 3.3 LPG vs Biogas or Solar
-
LPG: Available year-round regardless of weather.
-
Biogas/Solar: Renewable, but setup costs are high and performance is inconsistent without sun or organic waste.
4. Why LPG Is Still Widely Adopted in Developing Countries
In places like India, Nepal, Bangladesh, and African nations, LPG adoption has surged due to:
-
Widespread distribution networks
-
Schemes like Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY) that provide subsidized LPG connections
-
Lack of consistent electricity in rural areas
-
Cultural familiarity with gas-based cooking
5. Environmental Impact of LPG
While not a renewable fuel, LPG is a cleaner-burning hydrocarbon compared to:
-
Coal (higher CO₂, ash)
-
Kerosene (soot and toxic fumes)
-
Firewood (deforestation, indoor air pollution)
LPG is seen as a "transition fuel"—cleaner than traditional sources while the world prepares for a fully renewable future.
6. Future of LPG in the Global Fuel Mix
LPG may eventually decline in usage, but in the near term it will remain:
-
A reliable backup where solar/electric fails
-
A key fuel in disaster recovery or off-grid situations
-
A support for hybrid cooking systems (e.g., solar + LPG)
Innovations like bio-LPG (made from organic waste) are also emerging, blending LPG's infrastructure with sustainable inputs.
7. Conclusion: Is LPG Still Worth It?
Yes—LPG remains a practical, flexible, and relatively clean fuel. It’s affordable, widely distributed, and easy to use. Until electric infrastructure, appliance affordability, and renewable access improve globally, LPG will continue playing a vital role in daily life—especially in emerging economies.